Almost all software developers use databases in their daily routines.
The inconveniences can come when you need to work with different types of databases or different versions. Fortunately, there is a common way to work with all popular databases.
Prerequirements: Linux, Docker.
1. Start database server and DB management tool
With docker, you can run whatever database you want without installation hassle.
Let’s take the PostgreSQL db as an example.
Run
✦❯ docker run --name some-postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pswd -e POSTGRES_USER=user -e POSTGRES_DB=pdb -d --network=host postgres:15.3
70c2e363683fe9de108642e5f7140cd03d2ab0b117c8a3520c7a8ce6e7c10cca
After this command you should have the DB server started on your localhost
with created user: user and database: pdb on 5432 port.
To check it you can use telnet:
✦❯ telnet localhost 5432
Trying ::1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
2. Start DB management tool (Frontend)
Now we have a running PostgreSQL server and it’s time to use frontend. You need just start another docker container with adminer.
Run
✦❯ docker run -d --network=host adminer
c30e0215855e3926162749bde3a606a0ce20c4374abc688a665e604c78a64e66
The adminer is successfully run. Go to http://localhost:8080/
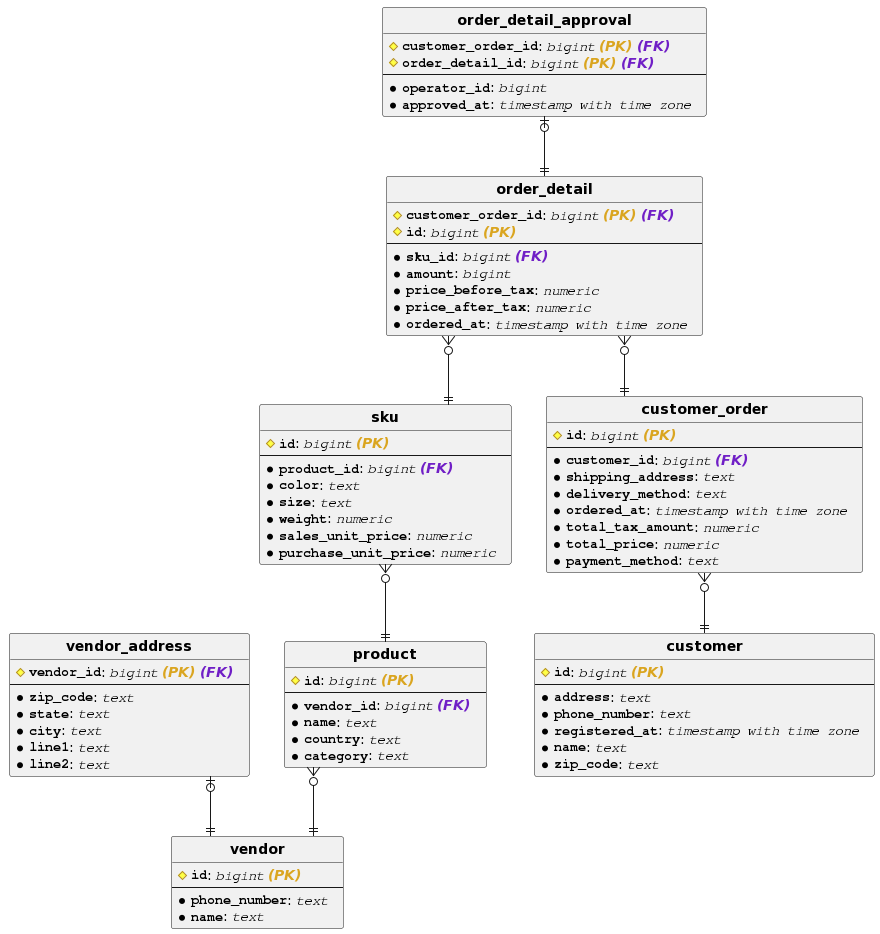
3. Analyze and share DB structure
To easily analyze and share with colleagues your DB structure you can use sqlant